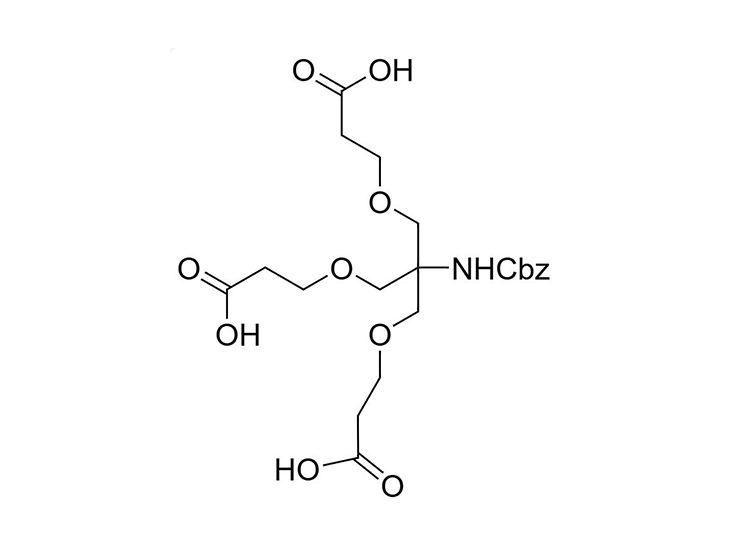
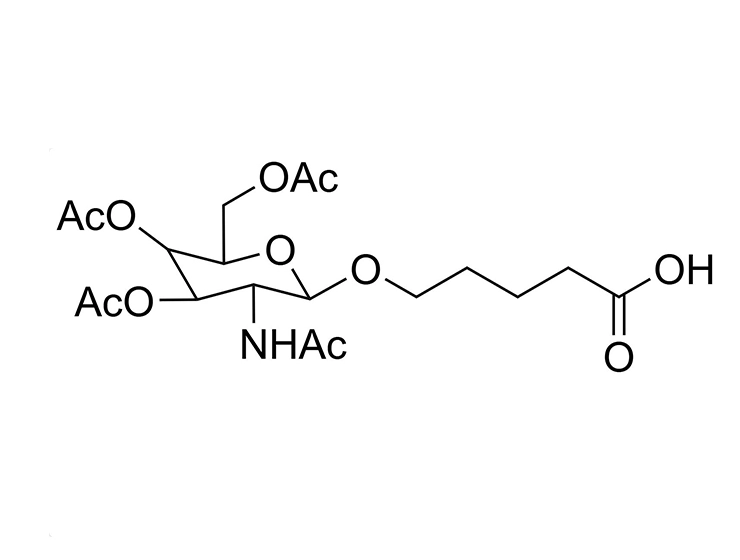
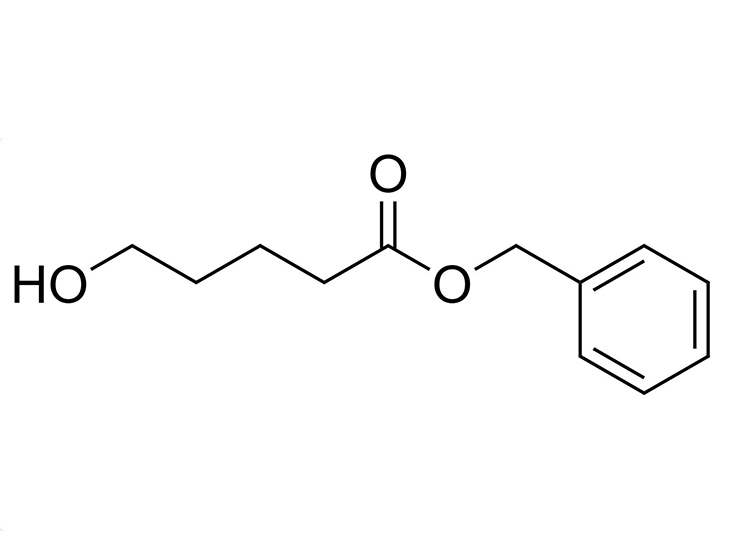
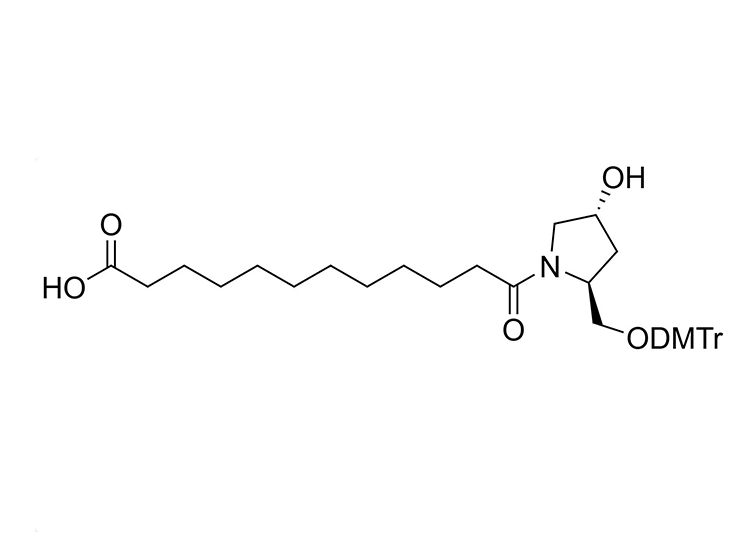
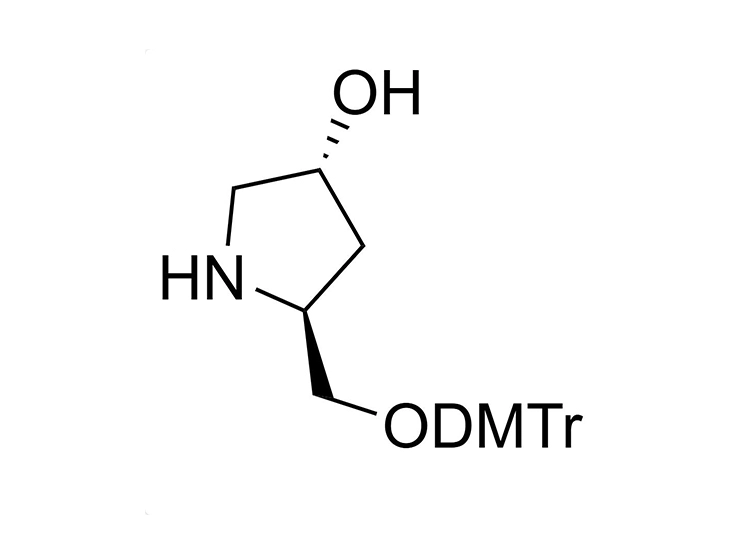
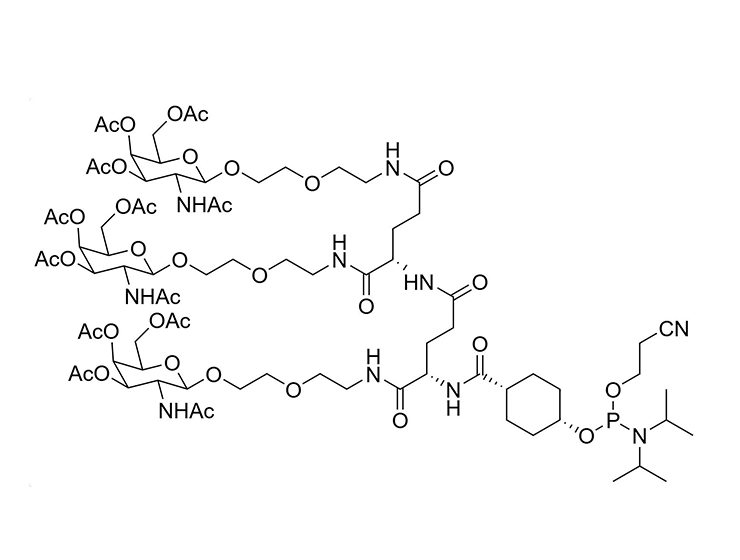
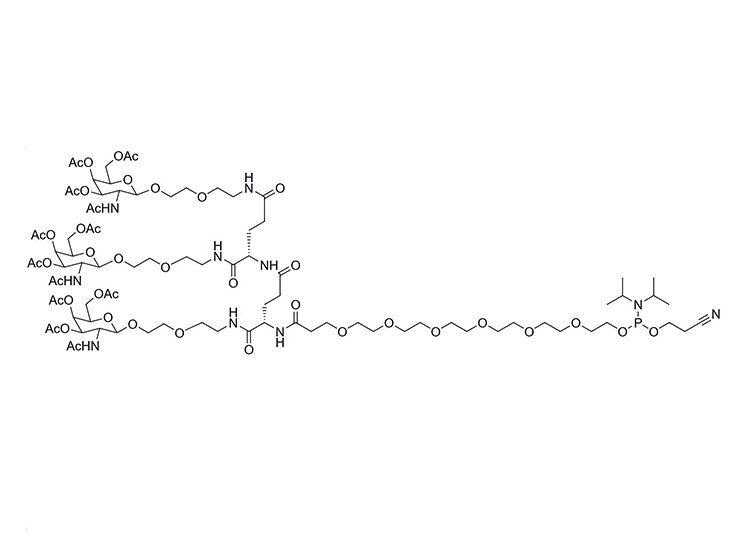
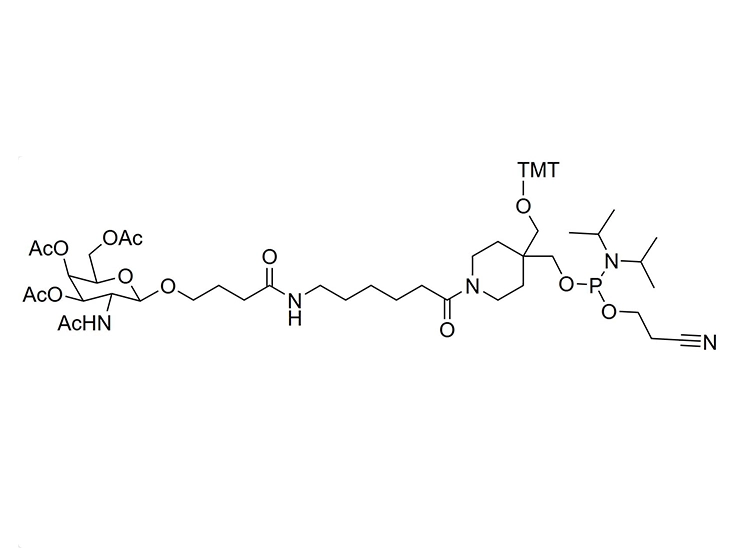
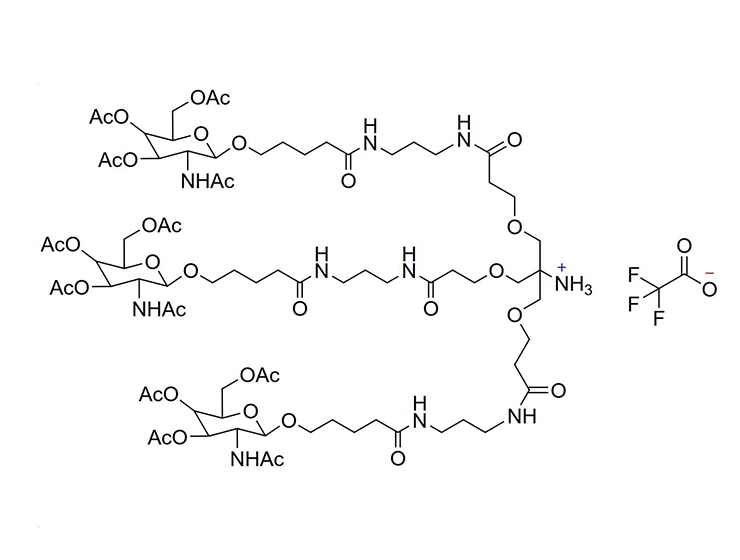
GalNAc (N-acetylgalactosamine) is a sugar molecule that plays a significant role in the delivery of drugs to the liver. It can be recognized and bound by the ASGPR (heparan sulfate proteoglycan receptor) on the surface of liver cells. Drugs can form complexes with GalNAc, which then efficiently bind to ASGPR and are internalized into hepatocytes. These complexes are released in acidic environments within the cell, allowing the drug molecules to be transported through cellular mechanisms such as endocytosis, leading to targeted delivery to the liver. This GalNAc-mediated delivery strategy enhances liver-targeted specificity, reducing distribution to other tissues and potentially decreasing side effects while improving therapeutic efficacy. As such, GalNAc serves as a valuable liver-targeting ligand in drug design and therapy.

 En
En Cn
Cn
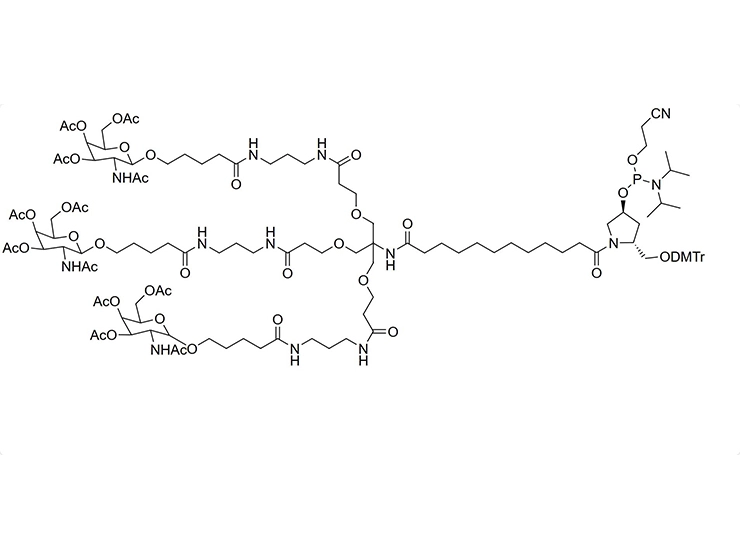
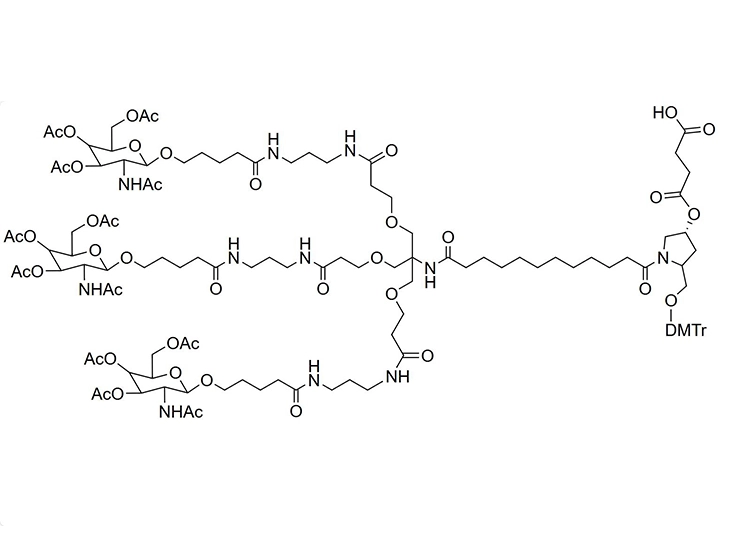
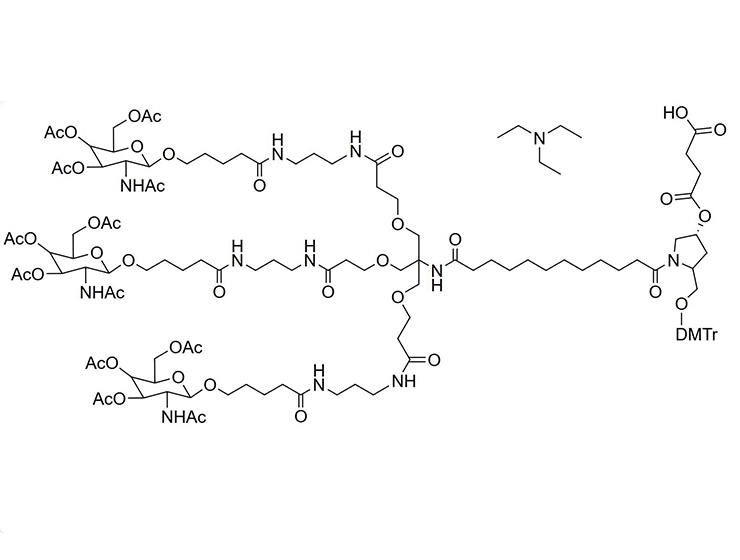
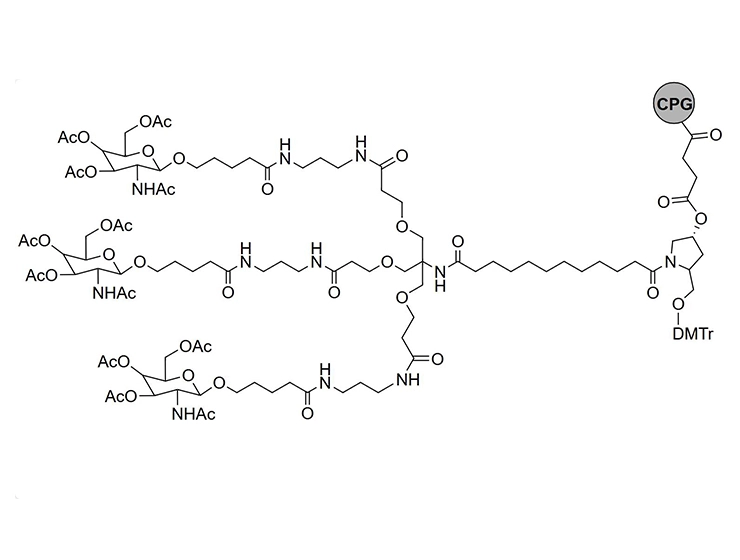
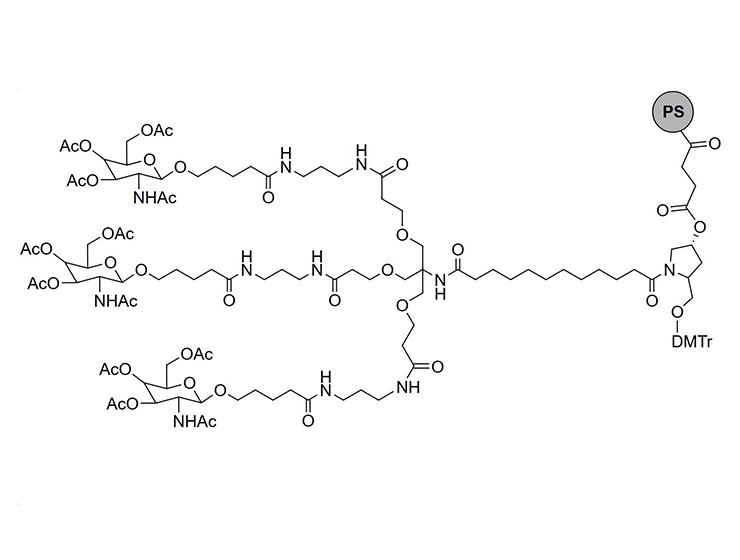
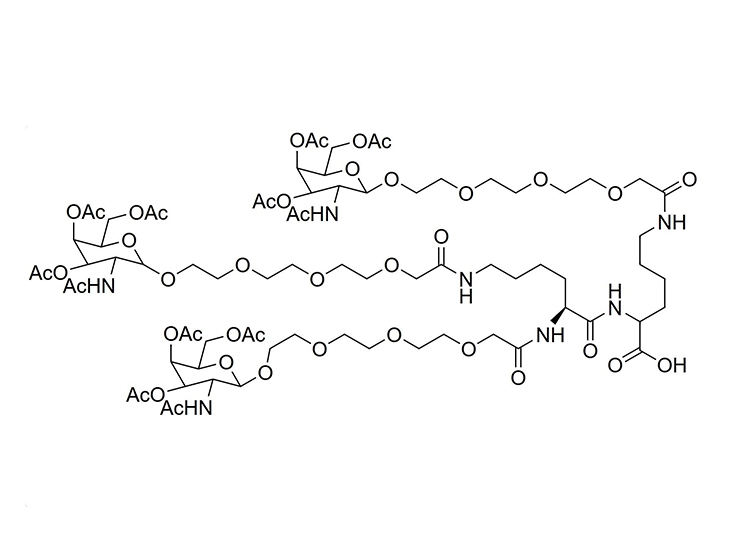
![3,3'-[[2-(Cbz-amino)-2-[[3-[[3-(Boc-amino)propyl]amino]-3-oxopropoxy]methyl]propane-1,3-diyl]bis(oxy)]bis[N-[3-(Boc-amino)propyl]propanamide] 3,3'-[[2-(Cbz-amino)-2-[[3-[[3-(Boc-amino)propyl]amino]-3-oxopropoxy]methyl]propane-1,3-diyl]bis(oxy)]bis[N-[3-(Boc-amino)propyl]propanamide]](/uploads/image/20240827/09/33-2-cbz-amino-2-3-3-boc-aminopropylamino-3-oxopropoxymethylpropane-13-diylbisoxybisn-3-boc-aminopropylpropanamide.webp)